
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease (can be passed on from person to person), This disease progresses in stages starting from the inflammation of the liver to severe liver damage or cirrhosis, this is due to a viral infection in the liver. The virus that causes the infection is called a Hepatitis C virus (HCV).
Book this really important test at your local top-quality labs through us at up to 50% discount. The lowest HCV test cost in India is ₹420 only.
Hepatitis C Test in India Through LabsAdvisor
|
Book your HCV test online to avail the exclusive offers and cashback!
Here are the simple steps to book your appointment at a discounted price.
- Click on the link given in the below table according to your preferred city.
- Choose the most suitable lab for your HCV test.
- Select your preferred date and time for your appointment.
- Enter the patient details and click submit.
- Congratulations! You have booked an appointment at a discounted price.
Book online yourself at any time of the day or night by clicking on the appropriate link in the table below
HCV Test Cost in India and Lab Details
We offer the discounted HCV test cost in over 20 Indian cities. Click on the link of your city below to choose a lab and make an online booking for home collection at a suitable time.
| Find HCV Test Labs & Book Appointment | Price starting from |
| HCV Test Price in Delhi | ₹420 |
| HCV Test Price in Gurgaon | ₹420 |
| HCV Test Price in Noida | ₹420 |
| HCV Test Cost in Bangalore | ₹680 |
| HCV Test Cost in Chennai | ₹4250 |
| HCV Test Price in Other Cities of India | ₹420 |

Frequently Asked Questions About HCV Test
What is Hepatitis C Virus?
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease (can be passed on from person to person), This disease progresses in stages starting from the inflammation of the liver to severe liver damage or cirrhosis, this is due to a viral infection in the liver. The virus that causes the infection is called a Hepatitis C virus (HCV).
What is Hepatitis C?
The Hepatitis C virus infects the liver, and in response, the immune system releases inflammatory chemicals, these chemicals stimulate the liver to produce a fibrous protein known as collagen to repair the damage, the collagen builds up quickly which creates scar tissue in the liver.
When the scar tissue builds up in the liver it is called fibrosis, fibrosis prevents blood from flowing in the liver cells, and in a span of time the liver cells die and the liver stops functioning normally. Not everyone infected with Hepatitis C (HCV) experiences the disease in the same way.
Hepatitis is contracted most commonly through blood or other body fluids that contain the blood of a person infected by the virus, and most people are unaware of it. There are immunizations for Hepatitis A & B but not for C.
If the infected person does not clear the virus in six months then the infection becomes chronic and is curable through medications, if untreated the chronic infection would lead to scarring, cirrhosis, and liver cancer and death in extreme cases.
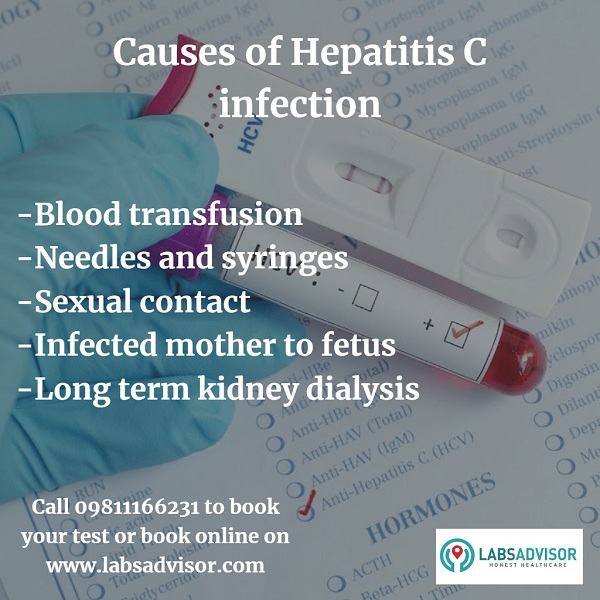
Causes of Hepatitis C infection
Hepatitis C is a disease borne by blood or other body fluids of an infected person. Listed below are the most common ways of how a person gets infected by Hepatitis C.
- Blood: When a person receives blood from a donor who already has Hepatitis C.
- Needles and Syringes: If a person injects drugs, or the same needle or syringe is used from a person infected by the HCV.
- Sexual Contact: When a person comes into sexual contact with a person infected by HCV without any precautions.
- Infected Mother: A child gets infected by HCV if the mother has the disease during pregnancy.
- Having Long-term Kidney Dialysis: Kidney failure can lead to a number of other health problems some of which can be fatal, kidney failure increases the risk of contracting Hepatitis C.
- HIV: HCV is common among people who have HIV; HCV viruses are transmitted in some of the same ways as HIV is transmitted, through the use of injection, drug use, sex without any precaution. When someone is infected with HIV and viral hepatitis, we say that they are “co-infected.”
What are the symptoms of Hepatitis C (HCV)?
Hepatitis C infection usually begins as an acute infection. It occurs a few weeks after exposure. This stage of the virus has no symptoms for many people who have the infection. If they do experience symptoms, it can begin weeks or months after exposure to the virus.
There are two stages of Hepatitis C symptoms:
- Acute stage
- Chronic stage
Symptoms during the Acute stage: (first six months of the disease).
People recently infected with HCV don’t have any symptoms. Those who do develop symptoms may have:
- Pain in the abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- dark urine(urine may appear dark yellow)
- fatigue
- fever
- change in stool color( stool may appear gray)
- pain in the joints
- nausea, vomiting
- When the skin and the eyes appear yellow it is known as jaundice, which is a sign that the liver isn’t working normally
For some people, the immune system destroys the virus during this phase. Most people progress to the chronic phases who are infected with the HCV virus.
Symptoms During the Chronic Stage:
The chronic phase of the disease starts after six months of the infection. In this stage, the body is not able to fight off the virus and they have a long-term infection.
Some people still don’t have any symptoms during the chronic phase. Often, people aren’t diagnosed until and unless they get screened while donating blood or their doctor detects high levels of liver enzymes during a routine blood test.
Cirrhosis and Liver Failure: Without treatment, scar tissue will eventually take over much of your liver. This is a chronic stage and is called cirrhosis.
The liver compensates for the damage at the first stage. But over time, the liver is so damaged or scarred that blood cannot flow easily through it, and the liver doesn’t work properly and is no longer able to filter toxic substances out of your blood.
People with cirrhosis have symptoms such as:
- easy bruising and bleeding
- confusion
- fatigue
- unexplained itchiness
- jaundice
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- swelling in the legs and abdomen
- weight loss
Cirrhosis also increases the risk of liver cancer.
How is Hepatitis C Diagnosed?
Hepatitis C (HCV) is generally diagnosed by a physical exam, by the symptoms, blood tests, and other studies, such as Fibro Sure. Sometimes the doctor may also ask for some imaging studies such as an ultrasound or CAT scan and a liver biopsy is also used.
If your doctor thinks that you may have hepatitis C, he or she may order you to go through some blood tests:
Screening for hepatitis C begins with a blood test that checks for the presence of HCV antibodies. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) test is a blood test that looks for the genetic material (RNA) of the virus that causes hepatitis or for the proteins (antibodies) the body makes against HCV. If you have a hepatitis C infection now or have had one in the past these proteins will be present in your blood. The test result is considered to be HCV antibody nonreactive if no HCV antibodies are found,. No further testing is required.
How is Hepatitis C treated?
Many Doctors have said that up to one out of four people who are infected with the hepatitis C virus will eventually be cured of the infection without any treatment. For these people, hepatitis C will be a short-term acute infection that goes away without any proper treatment or medication.
However, acute hepatitis C will develop into a chronic infection for most people and then they do require treatment. It is important to get tested for it if you think you might have been exposed since the virus often doesn’t have symptoms until after liver damage has taken place.
Treatment for hepatitis C depends on:
- How damaged is the liver?
- Other health conditions of the body?
- How much of the hepatitis C virus you have in your body?
- What type of hepatitis C you have?
Some methods of treatment are:
- Medications: Hepatitis C infection can be treated with some antiviral medications, intended to remove the virus from the body. The main purpose of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 – 13 weeks after you complete treatment. However, sometimes medicines used to treat hepatitis C can cause serious side effects, are expensive and don’t work for everyone.
- Liver transplantation: Liver transplantation may be an option if you have developed serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection. The surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver during the transplantation. However, in most cases, a liver transplant alone is not able to cure hepatitis C. The infection is most likely to return, requiring treatment with antiviral medication to prevent damage to the transplanted liver.
- Vaccinations: Many doctors recommend people to get vaccines against the hepatitis A and B viruses, although there is no vaccine for hepatitis C. This is because, during treatment of hepatitis C, these viruses can also lead to liver damage and cause complications.
Can hepatitis C be prevented?
There are two ways of preventing hepatitis C. “One way is to prevent people who don’t have it from getting it. The other way is to prevent people who have it from spreading it.”
The best prevention is to avoid exposure since you can’t prevent hepatitis C by getting vaccinated. Hepatitis C is a blood-borne pathogen so you can limit your chances of exposure by avoiding risky behavior. Some are mentioned below:
- Don’t share personal items like your razor, comb, or toothbrush.
- Use needle safety precautions if you use intravenous drugs, don’t share needles.
- If you have multiple sexual partners, practice safe sex.
- Not getting a tattoo in an unregulated environment.
- By eating a healthy and balanced diet and avoiding alcohol. Obesity and alcohol can make hepatitis C infections very difficult to treat.
- Women who are pregnant and have any symptoms of hepatitis C virus infection should speak to their doctor about having a screening test for the virus.
Interesting topics by LabsAdvisor that you may look for:-
- HBsAG Test Price in India
- CBC Test Cost in India
- Thyroid Function Test Cost in India.
- VDRL Test Cost in India






